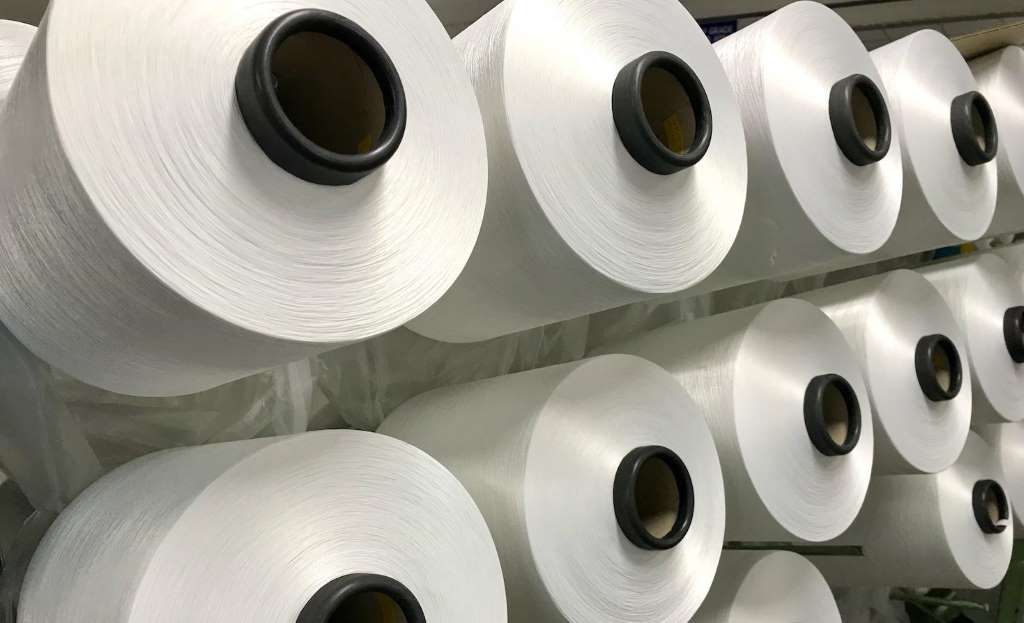
"Since the cotton producing regions have unique soil and agro-climatic conditions, the cotton produced by them are of different varieties and staple groups. The different varieties of cotton produced in India include medium staple, medium long staple and long staple. The country has largest area under Bt Cotton cultivation"
 In 2018-19, India produced around 21 per cent of the world’s cotton production. Most of the cotton is produced in nine major cotton growing states that include three diverse agro-ecological zones. Of this, the Northern zone comprises of Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan. The Central zone includes: Gujarat, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh while the Southern zone has Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
In 2018-19, India produced around 21 per cent of the world’s cotton production. Most of the cotton is produced in nine major cotton growing states that include three diverse agro-ecological zones. Of this, the Northern zone comprises of Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan. The Central zone includes: Gujarat, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh while the Southern zone has Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
A plethora of cotton variety
Since the cotton producing regions have unique soil and agro-climatic conditions, the cotton produced by them are of different varieties and staple groups. The different varieties of cotton produced in India include medium staple, medium long staple and long staple. The country has largest area under Bt Cotton cultivation. During the 2018-19 cotton seasons, the area under cotton cultivation was around 88 per cent of the total cultivable land available.
India has around 6.83 million tonne of cotton stock which includes domestic production, carryover stocks and imports. The total domestic consumption of cotton is 5.29 million metric tonne while exports are estimated to be worth around 0.85 million metric tonne.
Bangladesh, China among top importers
India mainly exports cotton to Bangladesh, China, Pakistan, Vietnam, Indonesia, Turkey, Taiwan and Thailand. During 2017-18, the country exported 1.15 million tonne of cotton which constituted about 15 per cent of total cotton produced in India.
Since 1994, cotton has also been a freely importable commodity in India. The country imported 0.27 million tonne of cotton during 2017-18 mainly from USA, Australia, Mali, Egypt, Cote D' Ivoire, Tanzania etc. These imports constituted less than 10 per cent of the total cotton consumption in India.
Sustainability schemes
The government of India is undertaking several measures to improve the quality and productivity of cotton and promote of sustainable cotton farming in the country. Due to these progressive steps taken by the government, the quality of Indian cotton has improved. Cotton yield too has improved from around 300 kg/hectare in the year 2002-03 up to 488 Kg/hectare currently.
The government is encouraging the cultivation of colored cotton in India. Many Indian scientists have noted that the desired parameter of colored cotton can be brought to the levels of white cotton to the satisfaction of the textile industry.
Contract farming is being encouraged and state-of-art technology to make the country self-sufficient in ELS cotton. The government is also kick-starting the process of bringing about a tangible improvement in production of ELS varieties of cotton. In addition to the above, India is also focusing on improvement of quality, demonstration of best practices for reducing the contamination of cotton, developing new varieties of cotton, increasing the production of Organic cotton and its’ certification in India.
Currently, India has the largest area under organic cotton cultivation in the world. The country ensures the genuineness and quality of organic production system, through National Programme for Organic Production by the Agricultural and Processed Foods Products Export Development Authority (APEDA). This national programme involves the accreditation programme for Certification Bodies, standards for organic production, promotion of organic farming, etc
India processes cotton by using double roller gin which preserves the inherent qualities of fiber, besides protecting the fiber length, providing undamaged clean seed and making Indian cotton better for spinning. Special attributes of roller ginning in India enables production of cotton fiber length up to 32.5 mm which is most suitable for spinning industry in production of higher counts of yarns.
Schemes for boosting quality and technology
The government is introducing mandatory bale testing and quality labeling/bale tagging system which would ensure traceability of cotton bales with essential details like year of manufacture, lot number, bale number, weight and various quality parameters. It has also introduced developmental schemes covering the entire textile value chain such as Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme, Powerloom Development schemes, Schemes of Integrated Textile Parks and Integrated Processing Development Scheme for increased consumption of cotton and other fibers.